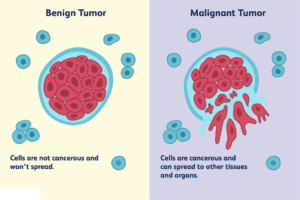
Malignancy refers to the presence of cancerous cells that have the ability to spread to other sites in the body (metastasize) or to invade nearby (locally) and destroy tissues. Malignant cells tend to have fast, uncontrolled growth and do not die normally due to changes in their genetic makeup.
A malignant tumor is a group of diseased cells defined by one of three characteristics: uncontrolled growth, invasion and damage of healthy cells, or metastasizing (spreading) to other organs of the body.
The most appropriate course of treatment is determined by the size, location, and stage of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Chemotherapy, radiation, hormone therapy, and surgery (or combinations of these treatments) are the most common methods offered to patients.
Depending on the location, surgery is sometimes the most effective option to remove the tumor and prevent a recurrence. Some patients add alternative therapies, such as natural remedies, massage, reiki, or dietary changes, to their traditional course of treatment.
Dr. Priya Nanda provide best Gynaecology Service for Malignant Tumor at Shreya Hospital in shalimar garden.
Symptoms and Causes
People with malignant neoplasms usually have varying symptoms depending on where the tumor is located. For example, someone with malignant neoplasm of their breast may notice breast pain or abnormal nipple discharge. People with malignant neoplasm of their colon might have abdominal pain or notice changes in their stool (poop). Those with malignant neoplasm of the skin may develop sores or lesions on their skin.
There are also general symptoms that people with cancerous tumors may experience, including:
- Fatigue.
- Shortness of breath.
- Anemia.
- Diarrhea.
- Weight loss.
- Drenching night sweats.
- Abnormal lumps or bumps.
Causes
We know that malignant neoplasms form when cells grow and divide faster than they should. But experts don’t know why this happens in the first place. But there are certain risk factors associated with malignant neoplasms, including:
- Smoking.
- Genetics.
- Obesity.
- Excessive alcohol use.
- Chemical toxins.
- Excessive exposure to radiation.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays.